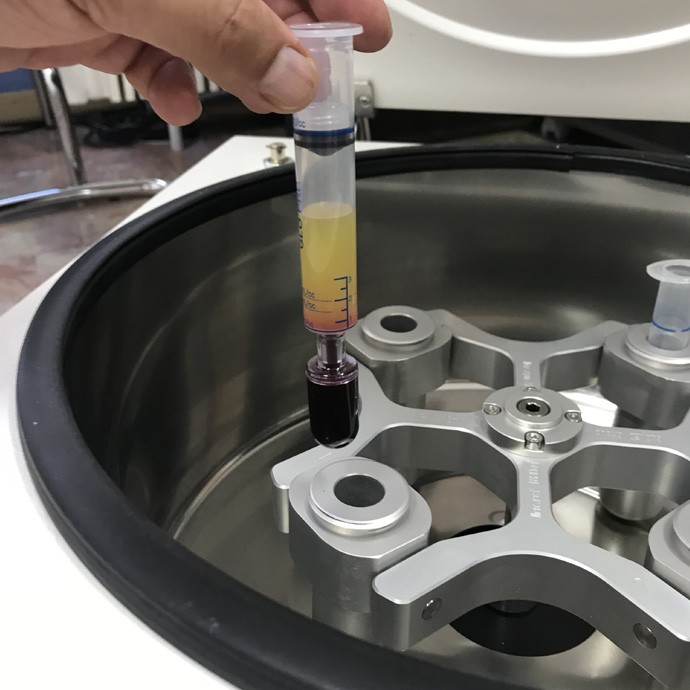
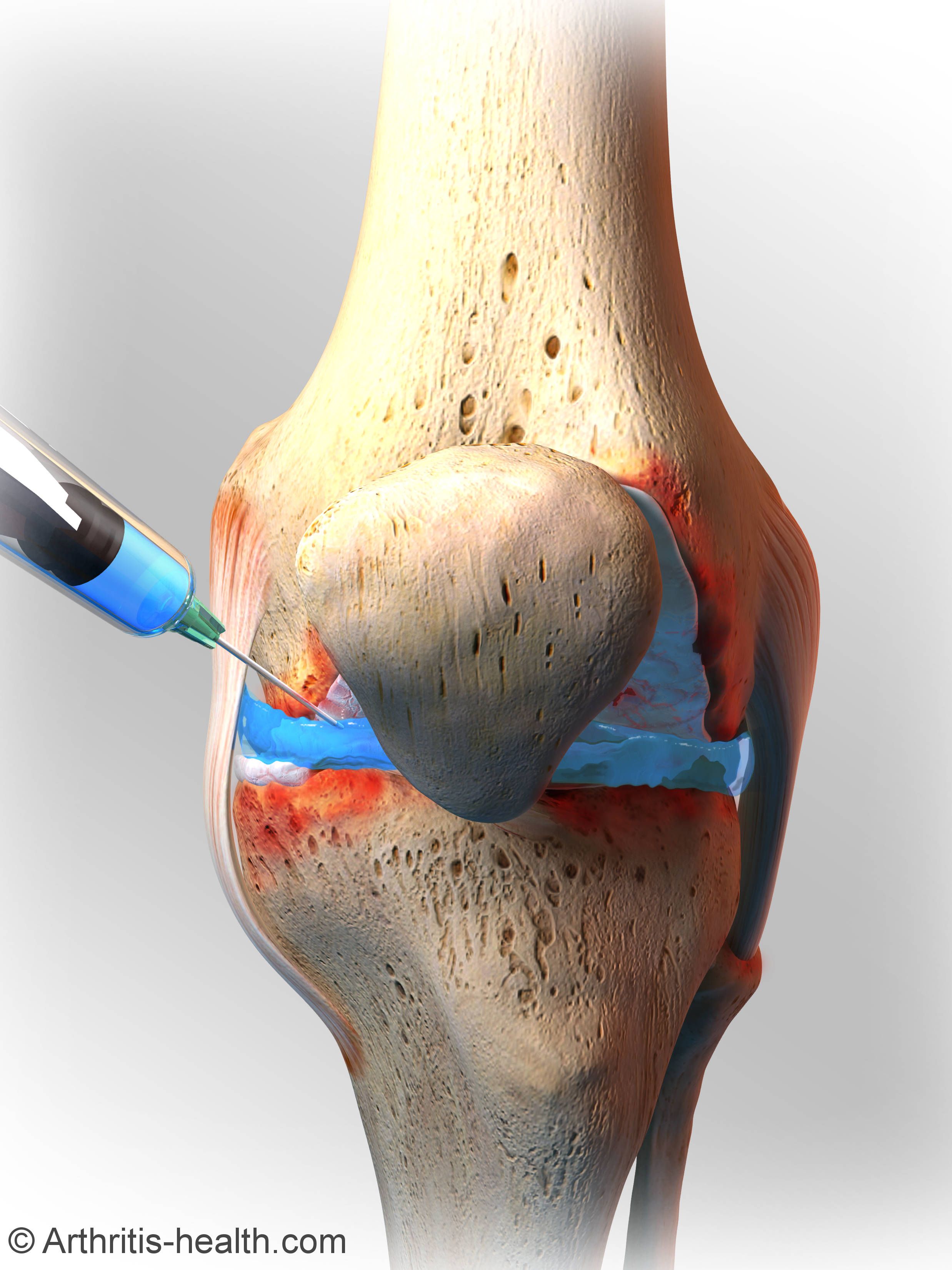
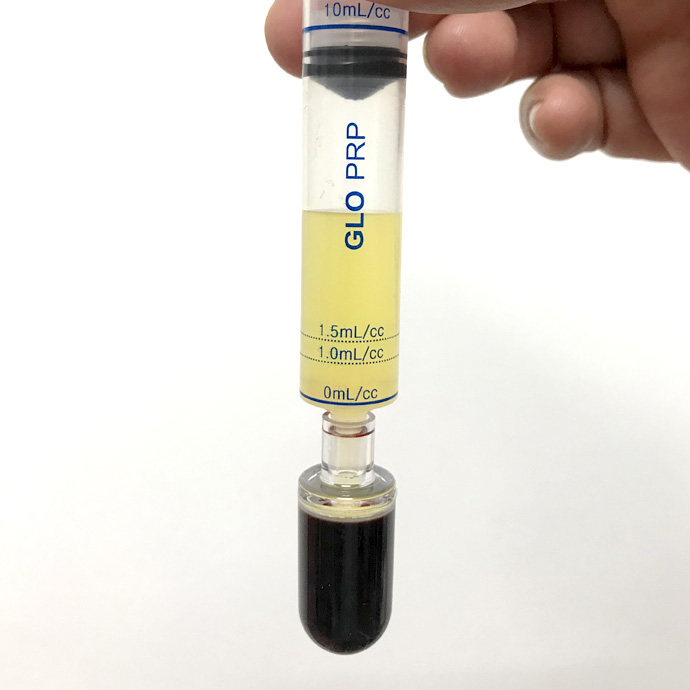
PRPs have proven their protective and anti-inflammatory properties on articular cartilage. Intra-articular injections with PRP transport many bioactive mediators into an autologous fibrin network, which are gradually released and improve pain, mobility and stiffness of the affected joint.
Platelet-derived growth factors, along with plasma growth factors (hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1)), stimulate cell proliferation as well as migration and matrix synthesis. Thus, PRP injection delivers growth factors locally while simultaneously mimicking and enhancing the spontaneous therapeutic response in injured areas and in special cell niches which would otherwise be inaccessible.
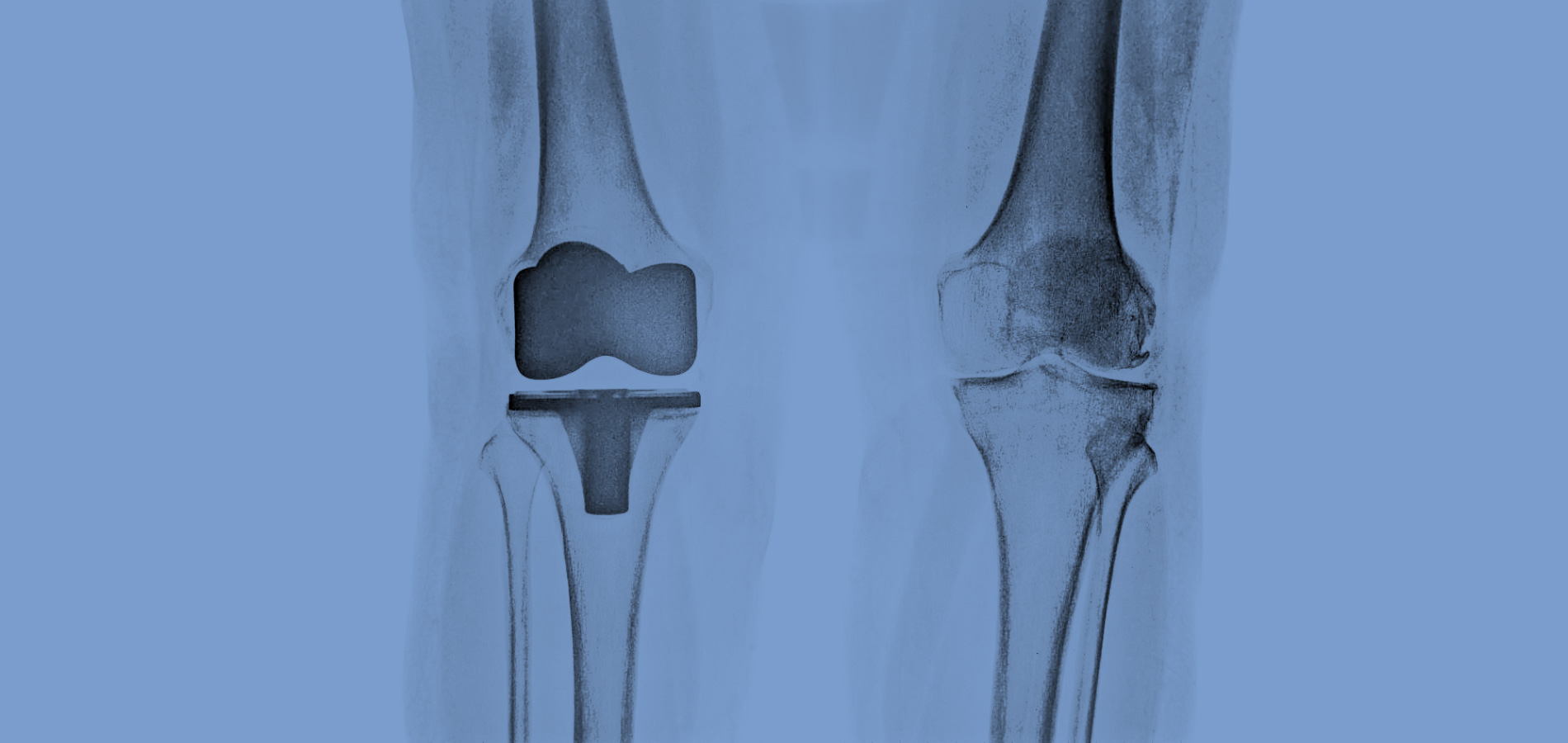
Recent studies highlight the important role of the subchondral bone in the role of arthritis. Separation of subchondral bone with articular cartilage appears to disrupt joint homeostasis by creating an inflammatory environment. Injecting PRP into the hypodermic bone helps restore the balance of articular homeostasis because growth factors aid the mechanical and biological connectivity of the tissues (transforming growth factor-b).