OSTEOARTHRITIS
OSTEOARTHRITIS
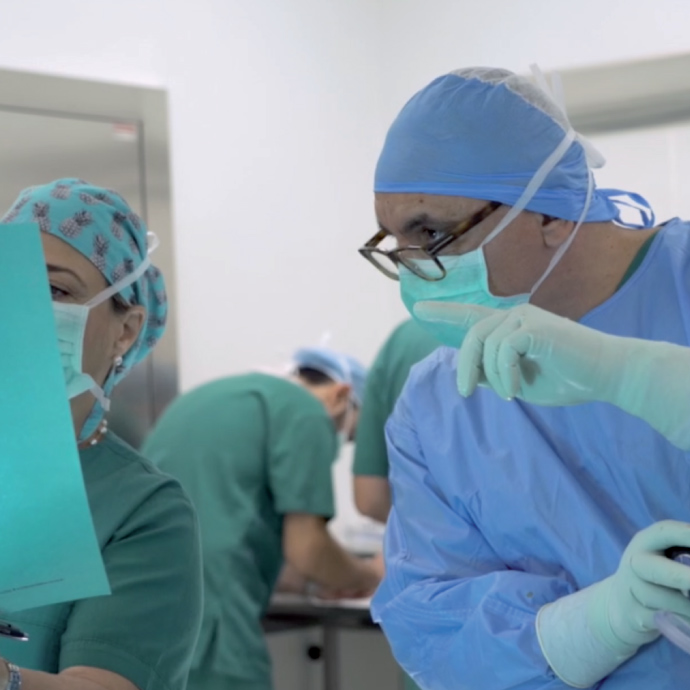
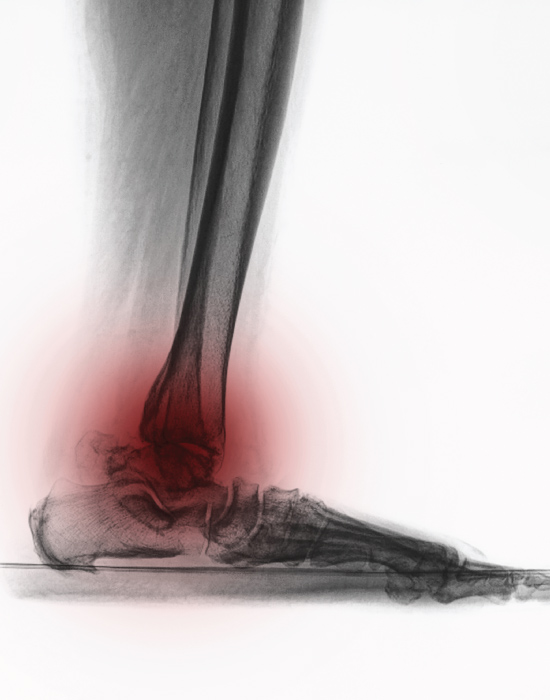
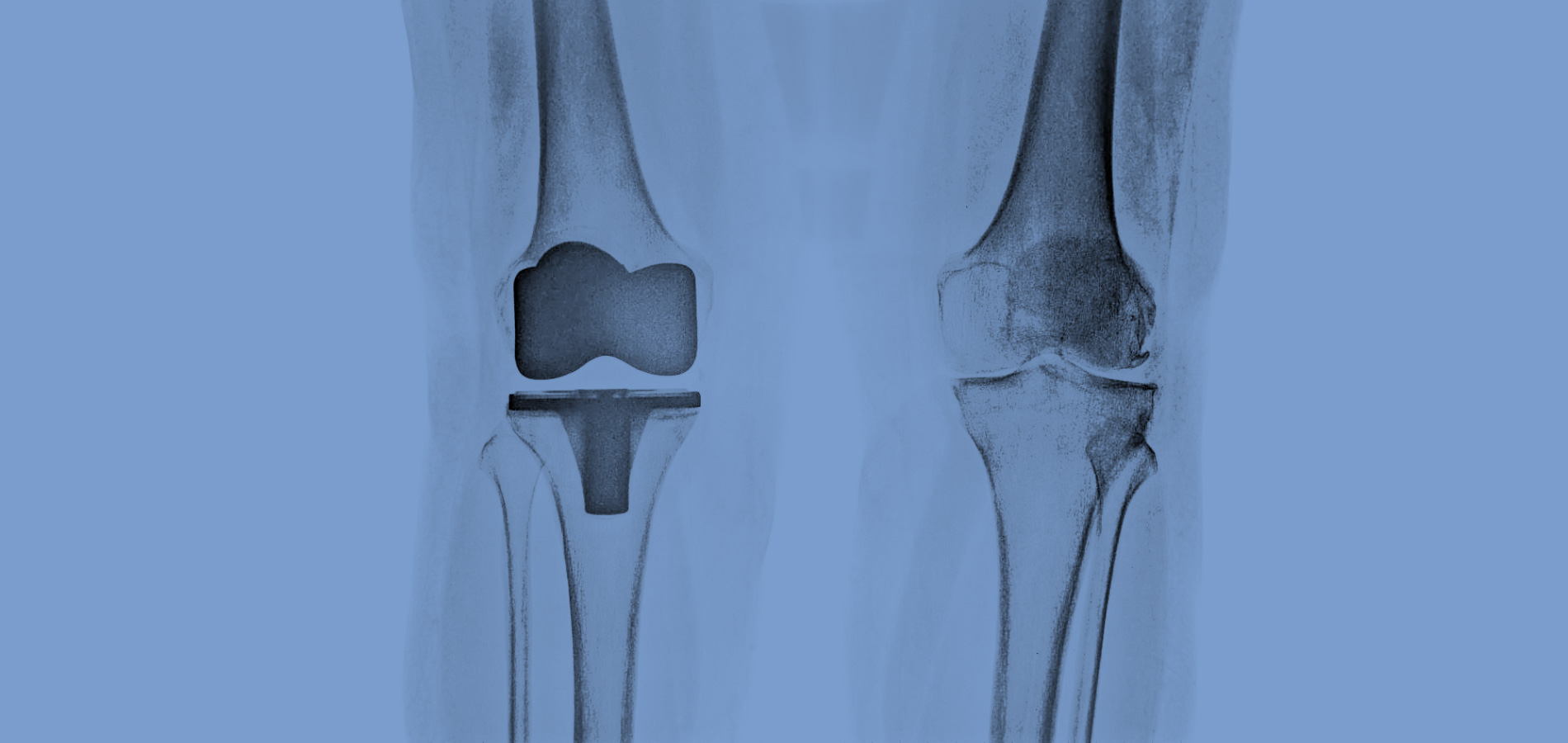
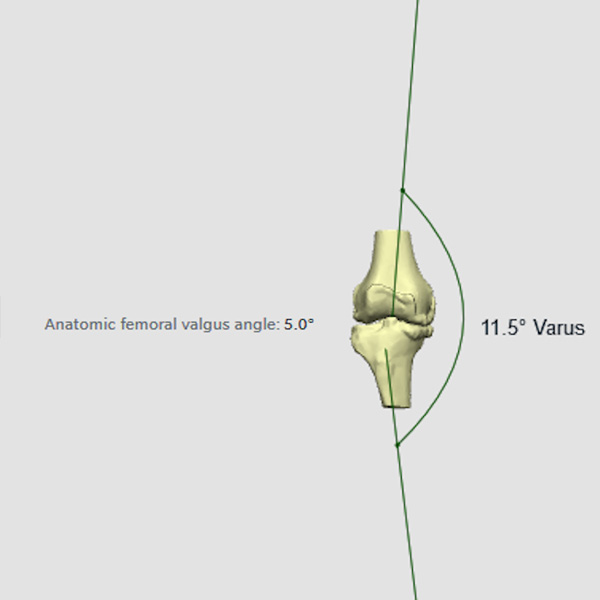
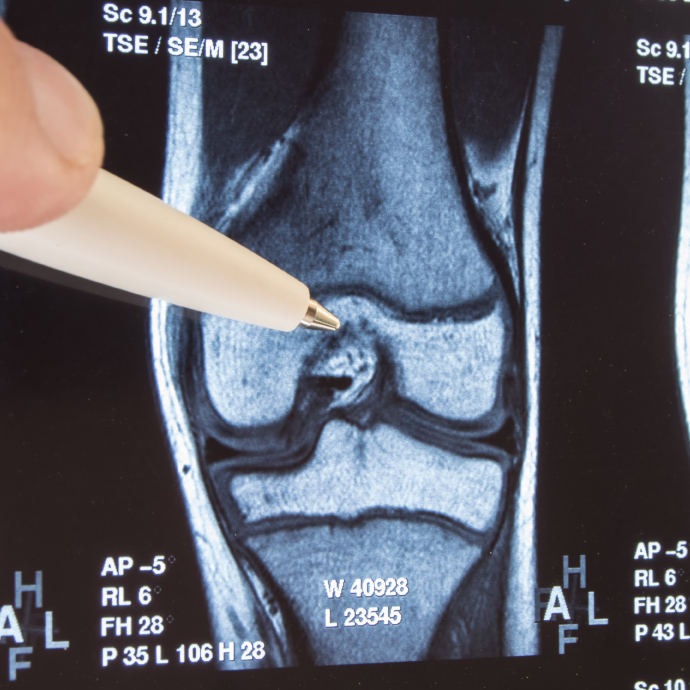
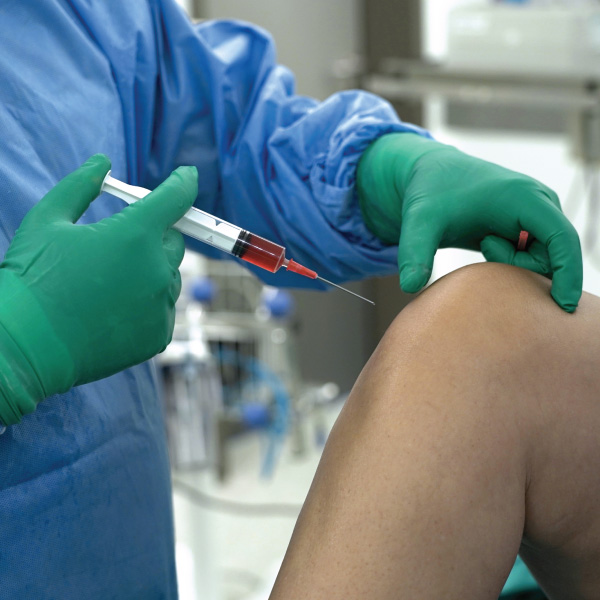
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a chronic, prevalent, debilitating joint disease characterized by progressive cartilage degradation, subchondral bone remodeling, bone marrow lesions, meniscal damage, and synovitis. It occurs mainly in the lower extremities but also occurs in the upper extremities and the spine - spondylarthritis. Due to the increase in the average life expectancy, osteoarthritis is now a disease that affects a large part of the population. The predisposing factors for the onset and progression of the disease are the high body weight, the individual's work, previous joint injuries as well as heredity. It occurs more often in women than in men.