OSTEOARTHRITIS TREATMENT WITH STEM CELLS FROM:
BONE MAROW STEM CELLS
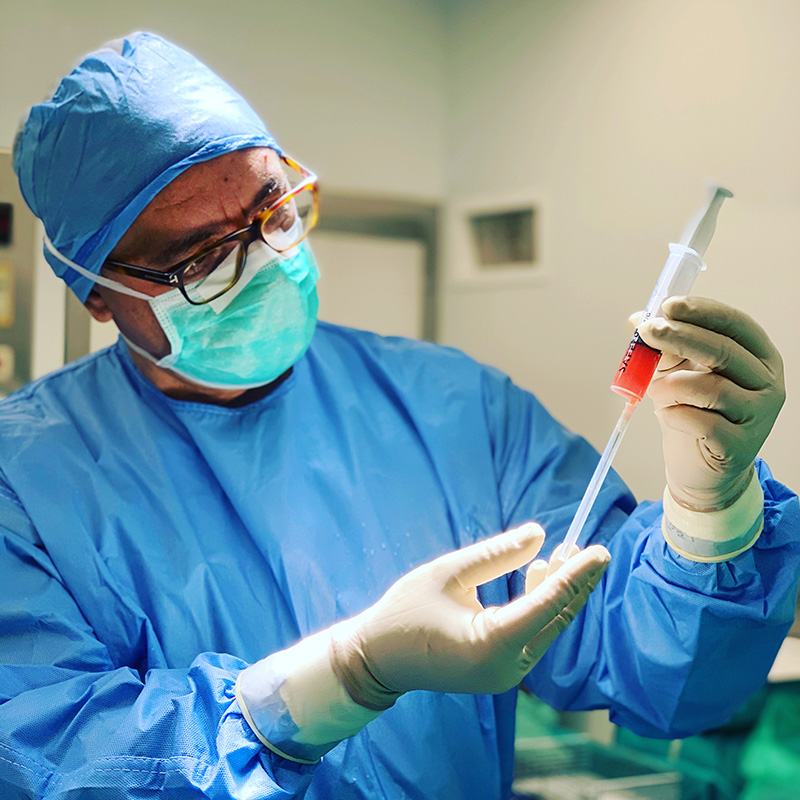
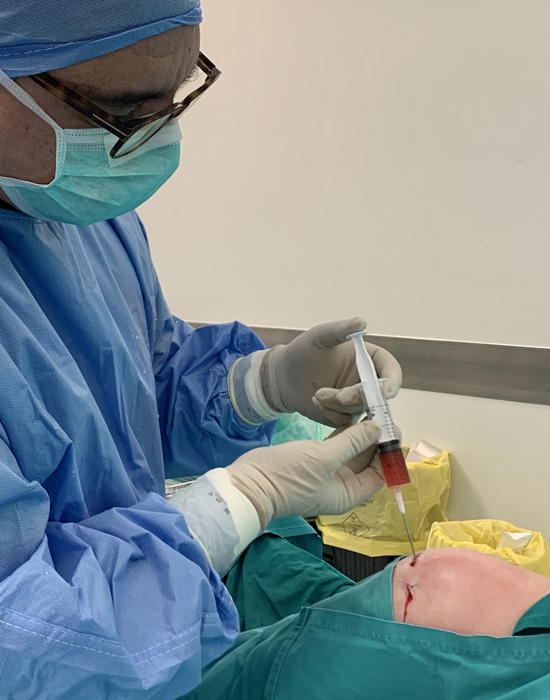
The bone marrow procedure is performed under surgical conditions by the pelvis (bone marrow aspiration). The patient is under light sedation. The quantity obtained does not exceed 20 cc. Immediately after aspiration, special processing of the bone marrow begins, resulting in the isolation of stem cells (3-4cc), which are injected into the affected joint. The total time from aspiration, processing and injection does not exceed 20 minutes. The patient leaves the clinic with instructions to rest for 48 hours.
ADIPOSE TISSUE
The adipose tissue is taken from the patient's abdomen where it is usually found in sufficient quantity. With a special trocar, 2-3cc of adipose tissue is obtained and sent directly to a specialist regenerative biotechnology company where the stem cells are isolated, cultivated and proliferated for approximately 5 weeks to achieve a sufficient number, usually twenty million stem cells. After weeks, the stem cells are injected into the affected joint. The whole procedure is done at the medical office and does not require an introduction to the clinic. Stem cell therapy can be ideally combined with arthroscopic procedure to correct all areas of articular cartilage damage as well as the cause of the damage (neglected torn of meniscus or anterior cruciate ligament).
Osteoarthritis has for many years been a disease for which medicine could only administer painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. Nowadays, knowledge of the pathogenesis of the disease as well as the evolution of biotechnology enables the specialist orthopedic surgeon to interfere with the development of the disease, relieve pain and stiffness and improve the quality of life of patients.